Configuring GitHub
Visit config-ui: http://localhost:4000.
Step 1 - Add Data Connections
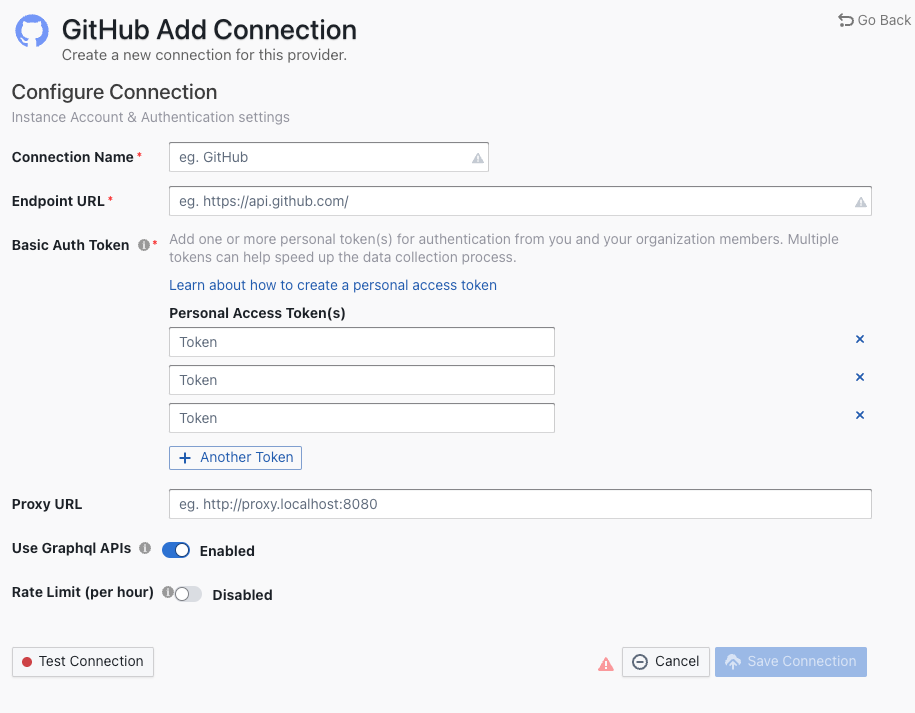
Connection Name
Name your connection.
Endpoint URL
This should be a valid REST API endpoint, eg. https://api.github.com/. The URL should end with /.
Auth Token(s)
You can use one of the following GitHub tokens: personal access tokens(PATs) or fine-grained personal access tokens.
GitHub personal access tokens(Recommended)
Learn about how to create a GitHub personal access token. The following permissions are required to collect data from repositories:
repo:statusrepo_deploymentread:userread:org
However, if you want to collect data from private repositories, the following permissions are required:
reporead:userread:org
The difference is that you have to give full permission for repos, not just repo:status and repo_deployment.
The data collection speed is restricted by the rate limit of 5,000 requests per hour per token (15,000 requests/hour if you pay for GitHub enterprise). You can accelerate data collection by configuring multiple personal access tokens. Please note that multiple tokens should be created by different GitHub accounts. Tokens belonging to the same GitHub account share the rate limit.
Fine-grained personal access tokens
Note: this token doesn't support GraphQL APIs. You have to disable Use GraphQL APIs on the connection page if you want to use it. However, this will significantly increase the data collection time.
If you're concerned with giving classic PATs full unrestricted access to your repositories, you can use fine-grained PATs announced by GitHub recently. With fine-grained PATs, GitHub users can create read-only PATs that only have access to repositories under certain GitHub orgs. But in order to do that, org admin needs to enroll that org with fine-grained PATs beta feature first. Please check this doc for more details. The token should be granted read-only permission for the following entities.
ActionsContentsDiscussionsIssuesMetadataPull requests
Use Graphql APIs
If you are using github.com or your on-premise GitHub version supports GraphQL APIs, toggle on this setting to collect data quicker.
- GraphQL APIs are 10+ times faster than REST APIs, but they may not be supported in GitHub on-premise versions.
- Instead of using multiple tokens to collect data, you can use ONLY ONE token because GraphQL APIs are quick enough.
Proxy URL (Optional)
If you are behind a corporate firewall or VPN you may need to utilize a proxy server. Enter a valid proxy server address on your network, e.g. http://your-proxy-server.com:1080
Fixed Rate Limit (Optional)
DevLake uses a dynamic rate limit to collect GitHub data. You can adjust the rate limit if you want to increase or lower the speed.
The maximum rate limit for GitHub is 5,000 requests/hour (15,000 requests/hour if you pay for GitHub enterprise). Please do not use a rate that exceeds this number.
Test and Save Connection
Click Test Connection, if the connection is successful, click Save Connection to add the connection.
Step 2 - Setting Data Scope
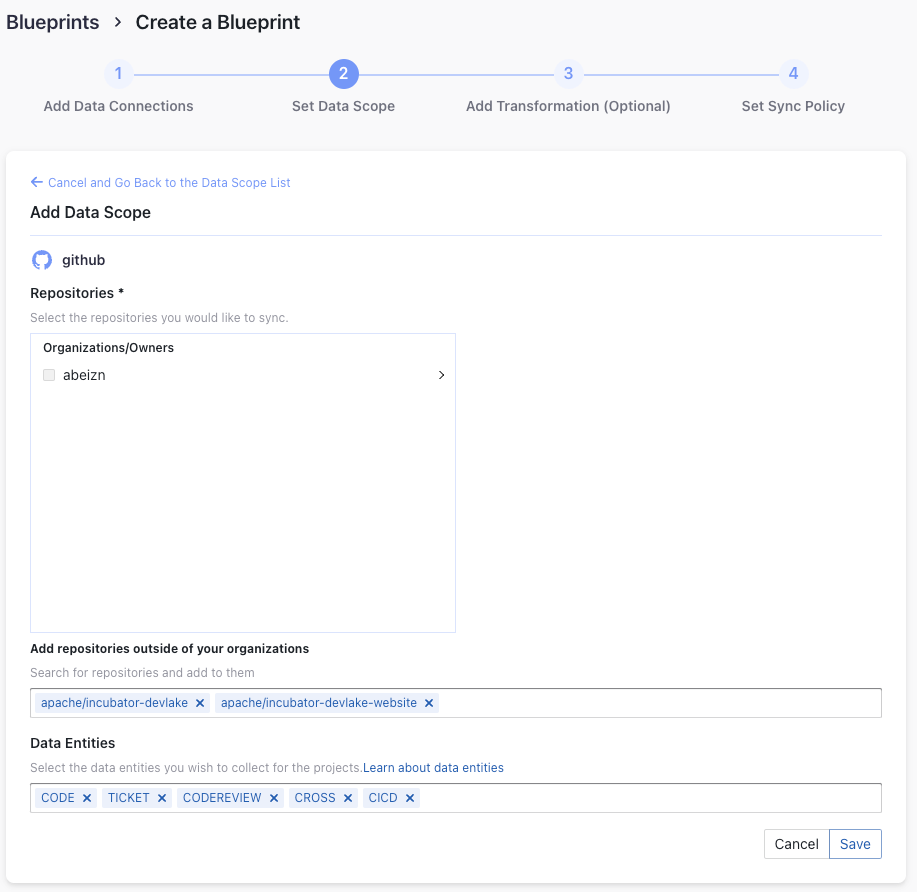
Projects
Enter the GitHub repos to collect. If you want to collect more than 1 repo, please separate repos with comma. For example, "apache/incubator-devlake,apache/incubator-devlake-website".
Data Entities
Usually, you don't have to modify this part. However, if you don't want to collect certain GitHub entities, you can unselect some entities to accelerate the collection speed.
- Issue Tracking: GitHub issues, issue comments, issue labels, etc.
- Source Code Management: GitHub repos, refs, commits, etc.
- Code Review: GitHub PRs, PR comments and reviews, etc.
- CI/CD: GitHub Workflow runs, GitHub Workflow jobs, etc.
- Cross Domain: GitHub accounts, etc.
Step 3 - Adding Transformation Rules (Optional)
Without adding transformation rules, you can still view the "GitHub Metrics" dashboard. However, if you want to view "Weekly Bug Retro", "Weekly Community Retro" or other pre-built dashboards, the following transformation rules, especially "Type/Bug", should be added.
Each GitHub repo has at most ONE set of transformation rules.
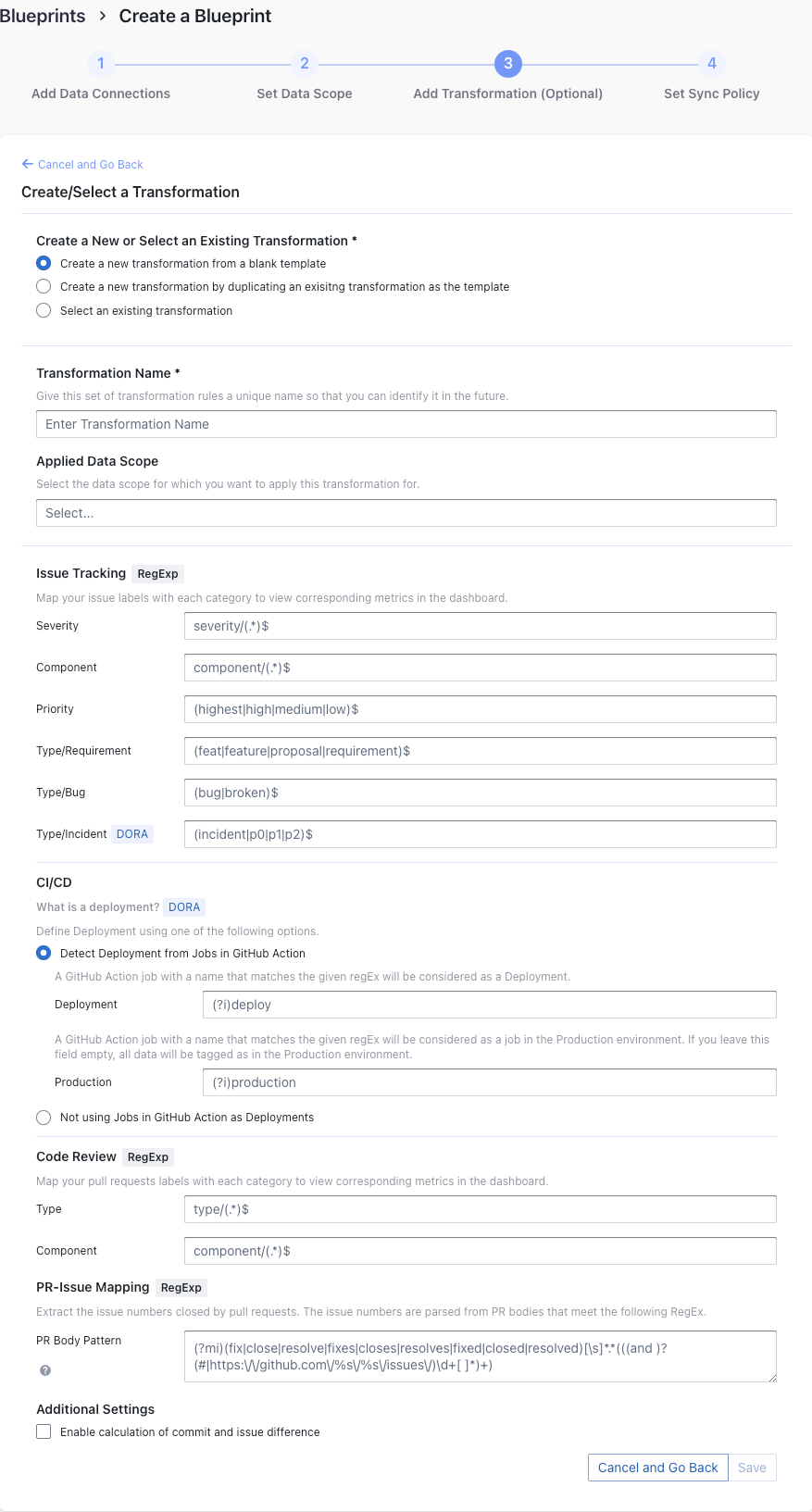
Issue Tracking
Severity: Parse the value of
severityfrom issue labels.- when your issue labels for severity level are like 'severity/p0', 'severity/p1', 'severity/p2', then input 'severity/(.*)$'
- when your issue labels for severity level are like 'p0', 'p1', 'p2', then input '(p0|p1|p2)$'
Component: Same as "Severity".
Priority: Same as "Severity".
Type/Requirement: The
typeof issues with labels that match given regular expression will be set to "REQUIREMENT". Unlike "PR.type", submatch does nothing, because for issue management analysis, users tend to focus on 3 kinds of types (Requirement/Bug/Incident), however, the concrete naming varies from repo to repo, time to time, so we decided to standardize them to help analysts metrics.Type/Bug: Same as "Type/Requirement", with
typesetting to "BUG".Type/Incident: Same as "Type/Requirement", with
typesetting to "INCIDENT".
CI/CD
This set of configurations is used for calculating DORA metrics.
If you're using GitHub Action to conduct deployments, please select "Detect Deployment from Jobs in GitHub Action", and input the RegEx in the following fields:
- Deployment: A GitHub Action job with a name that matches the given regEx will be considered as a deployment.
- Production: A GitHub Action job with a name that matches the given regEx will be considered a job in the production environment.
A GitHub workflow run has many jobs. Each GitHub workflow run is converted to a cicd_pipeline in the domain layer and each GitHub Action job is converted to a cicd_task in the domain layer.
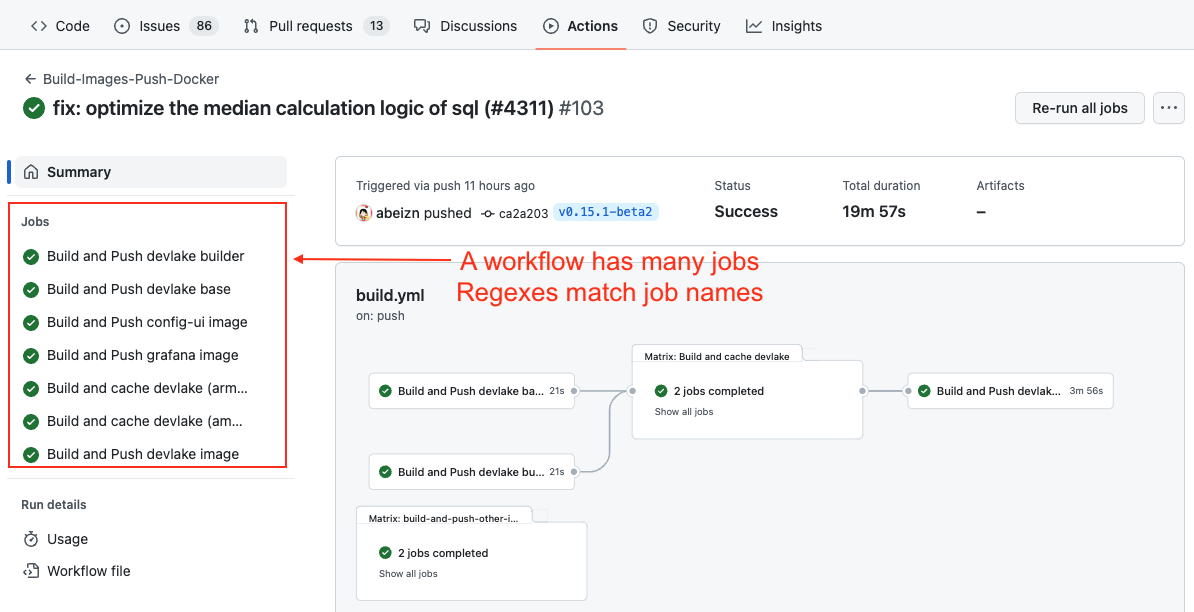
The deployment and production regex is always applied to the records in the cicd_tasks table.
You can also select "Not using Jobs in GitHub Action as Deployments" if you're not using GitHub action to conduct deployments.
Code Review
Type: The
typeof pull requests will be parsed from PR labels by given regular expression. For example:- when your labels for PR types are like 'type/feature-development', 'type/bug-fixing' and 'type/docs', please input 'type/(.*)$'
- when your labels for PR types are like 'feature-development', 'bug-fixing' and 'docs', please input '(feature-development|bug-fixing|docs)$'
Component: The
componentof pull requests will be parsed from PR labels by given regular expression.
Additional Settings (Optional)
Tags Limit: It'll compare the last N pairs of tags to get the "commit diff', "issue diff" between tags. N defaults to 10.
- commit diff: new commits for a tag relative to the previous one
- issue diff: issues solved by the new commits for a tag relative to the previous one
Tags Pattern: Only tags that meet given regular expression will be counted.
Tags Order: Only "reverse semver" order is supported for now.
Please click Save to save the transformation rules for the repo. In the data scope list, click Next Step to continue configuring.
Step 4 - Setting Sync Frequency
You can choose how often you would like to sync your data in this step by selecting a sync frequency option or enter a cron code to specify your prefered schedule.
Troubleshooting
If you run into any problem, please check the Troubleshooting or create an issue