GitLab
Visit Config UI: http://localhost:4000.
Step 1 - Add Data Connections
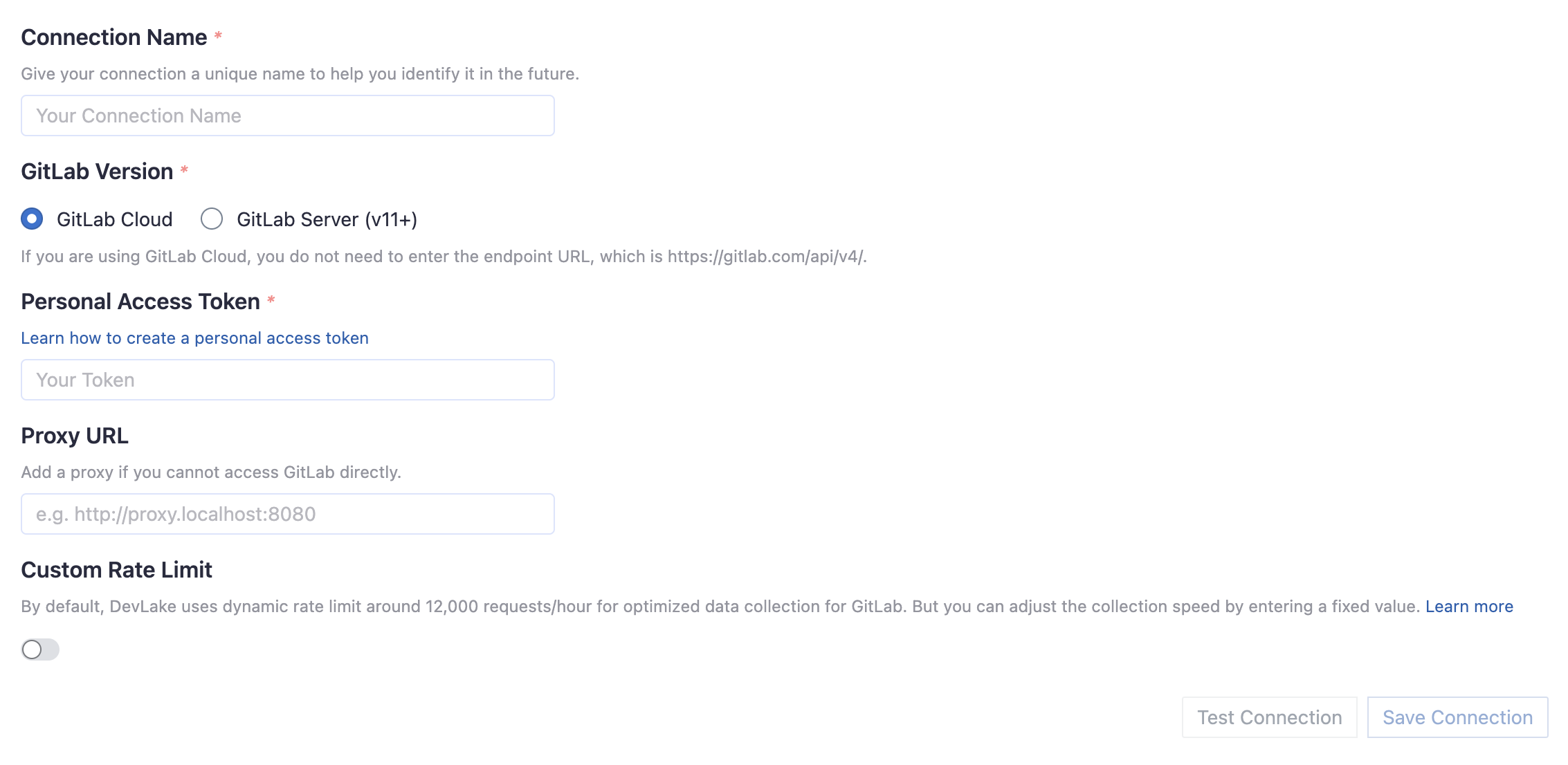
Connection Name
Give your connection a unique name to help you identify it in the future.
GitLab Version
Select if you use GitLab Cloud or GitLab Server (v11+).
Endpoint URL
This should be a valid REST API endpoint.
- If you use GitLab cloud, you do not need to enter the endpoint, which is always
https://gitlab.com/api/v4/. - If you GitLab Server (v11+), the endpoint will look like
https://gitlab.example.com/api/v4/. Please note: the endpoint URL should end with/.
Personal Access Token
Your GitLab personal access token (PAT) is required to add a connection. Learn about how to create a GitLab personal access token.
Personal Access Token Permissions
At least one of the following permissions is required to collect data from repositories:
apiread_api
You also have to double-check your GitLab user permission settings.
- Go to the Project information -> Members page of the GitLab projects you wish to collect.
- Check your role in this project from the Max role column. Make sure you are not the Guest role, otherwise, you will not be able to collect data from this project.
Proxy URL (Optional)
If you are behind a corporate firewall or VPN you may need to utilize a proxy server. Enter a valid proxy server address on your network, e.g. http://your-proxy-server.com:1080
Fixed Rate Limit (Optional)
DevLake uses a dynamic rate limit at around 12,000 requests/hour to collect GitLab data. You can adjust the rate limit if you want to increase or lower the speed.
The maximum rate limit for GitLab Cloud is 120,000 requests/hour. Tokens under the same IP address share the rate limit, so the actual rate limit for your token will be lower than this number.
For self-managed GitLab rate limiting, please contact your GitLab admin to get or set the maximum rate limit of your GitLab instance. Please do not use a rate that exceeds this number.
Test and Save Connection
Click Test Connection, if the connection is successful, click Save Connection to add the connection.
Step 2 - Setting Data Scope
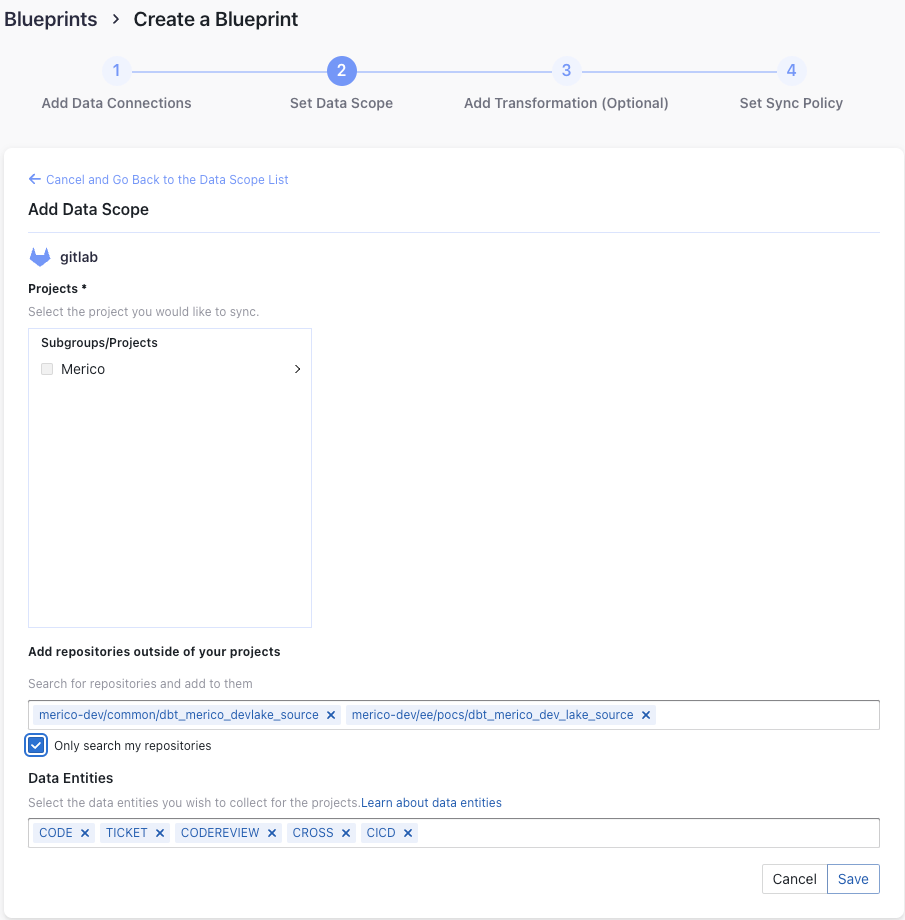
Projects
Choose the GitLab projects to collect. Limited by GitLab API, You need to type more than 2 characters to search.
- If you want to collect public repositories in GitLab, please uncheck "Only search my repositories" to search all repositories.
Data Entities
Usually, you don't have to modify this part. However, if you don't want to collect certain GitLab entities, you can unselect some entities to accerlerate the collection speed.
- Issue Tracking: GitLab issues, issue comments, issue labels, etc.
- Source Code Management: GitLab repos, refs, commits, etc.
- Code Review: GitLab MRs, MR comments and reviews, etc.
- CI/CD: GitLab pipelines, jobs, etc.
- Cross Domain: GitLab accounts, etc.
Step 3 - Adding Transformation Rules (Optional)
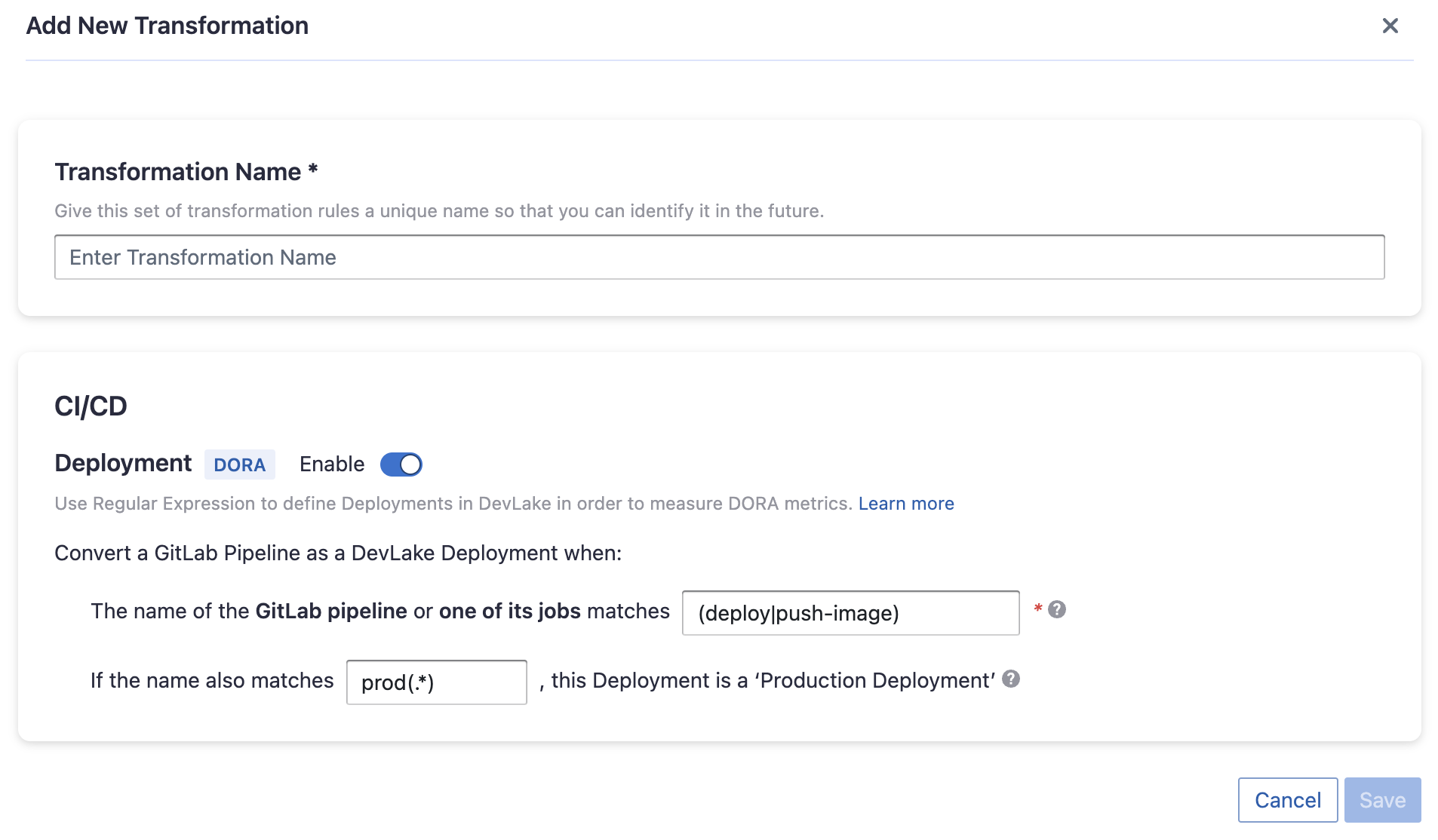
CI/CD
This set of configurations is used for calculating DORA metrics.
If you're using GitLab CI to conduct deployments, please select "Detect Deployment from Jobs in GitLab CI", and input the RegEx in the following fields:
- Deployment: The name of the GitLab pipeline or one of its jobs matches the given regEx will be considered as a deployment.
- Production: If the name also matches the PRODUCTION regEx, the deployment will be considered a PRODUCTION deployment.
By the above two fields, DevLake can identify a production deployment among massive GitLab CI pipelines.
Step 4 - Setting Sync Policy
You can choose how often you would like to sync your data in this step by selecting a sync frequency option or enter a cron code to specify your prefered schedule.
Troubleshooting
If you run into any problem, please check the Troubleshooting or create an issue